- Functional Food for your Genes
-
by k.mammasis
Immune Boosting products are currently at the forefront of the global pharma market and covid is definitely the highest contributor. There is no doubt that functional foods for immune are highly growing in popularity among those of you who are looking for natural alternatives to supplements for immune system boosting. Are you still wondering why functional foods are your best source? Read our latest article on the comparison between natural vs synthetic nutrients, why our functional foods outperform supplements and will improve your overall health in less than 3 months.
Can Specific Foods Boost the Immune System?
A strong immune system contributes to a person’s overall health. Organs, cells, tissues, and proteins make up the immune system.
These work together to carry out biological processes that combat pathogens, which are viruses, bacteria, and foreign substances that cause infection or disease. When the immune system comes into contact with a pathogen, an immunological reaction is elicited.
The immune system produces antibodies, which bind to pathogen antigens and kill them. Including certain functional foods in one’s diet may help to boost one’s immune system. Continue reading to learn 9 ways that will help you to boost your immune system through intelligent food choices.
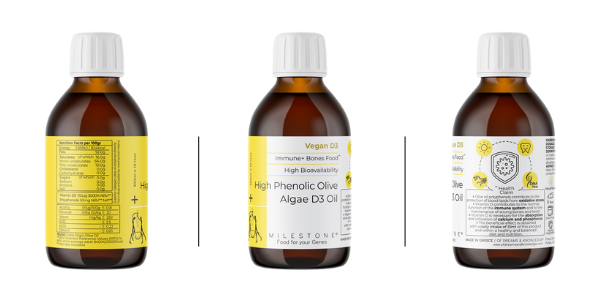
1. High Phenolic Olive + Algae Vitamin D3 Oil
Immune Boosting is among the most complex of natural processes in our body. It requires an equally complex synergy of functional food and psychology to deliver a great result. Our medical olive oil is combined with the best vegan D3 source on the planet in order to naturally supply you with 600 IU of Vitamin D3 plus many other bioactive compounds not found in conventional olive oil. Discover more about our strongest functional food for immune boost.
2. Pomegranate with Vegan Curcumin + Vitamin D3
The advanced Liquid Curcumin Extract is encased in tiny spheres called micelles which quickly enter the bloodstream and stay there far more effectively than the hundreds of turmeric supplements available on the general market. The addition of Vitamin D3 uplifts the anti-inflammatory response to even greater heights. All this uniquely combined with the nature’s most potent fruit, the pomegranate. Each bottle contains at least 25 healthy, high quality organic pomegranates. Learn more on how our pomegranate concentrate fortified with the best turmeric exact in the world, may help you in treating inflammation, but also serve as a natural immune booster through the synergistic combination with vitamin D3.
3. Blueberries
Blueberries include anthocyanin, a type of flavonoid with antioxidant characteristics that can help enhance a person’s immune system. According to a 2016 study 1, flavonoids have an important role in the immune defense mechanism of the respiratory tract. Researchers discovered that those who consumed foods high in flavonoids were less likely to get an upper respiratory tract infection, also known as the common cold, than those who did not.
4. Garlic
Garlic is a plant in the Allium (onion) family. Throughout history, the primary use of garlic was for its medical and therapeutic benefits. Sulfur molecules generated when a garlic clove is chopped, crushed, or chewed are responsible for the majority of its health advantages, according to scientists 2. Allicin is perhaps the most well-known of them. However, allicin is only available in fresh garlic after it has been sliced or crushed for a short period of time 3. One study investigated whether consuming garlic supplements containing allicin lowered the likelihood of catching a cold. The group of participants taking a placebo had more than double the number of colds between them than those taking the garlic supplements. However, the researchers concluded that more research is necessary to determine whether or not garlic can help to prevent colds 4.
5. Green tea
Flavonoids, a type of antioxidant, are abundant in both green and black teas. Green tea really shines when it comes to levels of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), another potent antioxidant. EGCG has been shown in trials to improve immunological function. A large portion of the EGCG in black tea is destroyed during the fermenting process. Green tea, on the other hand, is steamed rather than fermented, preserving the EGCG 5. Green tea is also high in the amino acid L-theanine. L-theanine may help your T cells produce germ-fighting chemicals.
6. Ginger
Ginger contains anti-inflammatory and antioxidative qualities, according to a review, and is very likely to provide health advantages. More research, however, is required to clarify whether or not it can effectively prevent sickness 6 7. The main bioactive ingredient in ginger is gingerol. It is responsible for a large portion of ginger’s therapeutic effects 8 9. According to studies, gingerol has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. For example, it may aid in the reduction of oxidative stress, which is caused by an excess of free radicals in the body.
7. Broccoli
Broccoli is a good source of vitamin C as well. It also contains powerful antioxidants like sulforaphane. For these reasons, it is an excellent vegetable to eat on a daily basis to boost immune system health 10. In addition, the antioxidant content of broccoli may be one of its main bonuses for human health 11. Broccoli also includes trace amounts of the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin, which may protect your eyes from oxidative stress and cellular damage 12.
8. Turmeric
For years, this bright yellow, bitter spice has been used as an anti-inflammatory in the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis 13. According to research, high amounts of curcumin, the compound that gives turmeric its unique color, can help reduce exercise-induced muscle damage 14. Based on other research, curcumin has the potential to be an immune booster and an antiviral 15. Discover the amazing health benefits of our curcumin extract, served on a delicious pomegranate base plus Vitamin D3. A true powerhouse of foods for immune.
9. Citrus Fruits
After catching a cold, most individuals reach for vitamin C. Because your body does neither make nor store it, you better consume it on a daily basis to maintain your health 16. This is due to the fact that it aids in the development of your immune system. Vitamin C is known to boost the formation of white blood cells, which are essential for combating infections 17. Its levels are high in almost all citrus fruits. With so many options, it’s simple to incorporate this vitamin into every meal. Citrus fruits that are popular include:
-
- oranges
- grapefruit
- clementines
- tangerines
- lemons
- limes
Most adults should consume the following quantity on a daily basis: Women should take 75 mg – Men should take 90 mg. Also, while vitamin C may help you recover faster from a cold, there is no proof that it is beneficial against the new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2.
MILESTONE® Tip: Squeeze your fresh citrus fruits and add a cup of our Pomegranate Concentrate with Turmeric Extract and Vitamin D3. It will power up your whole day!
Variety is Key to Proper Nutrition
The key to good nutrition is variety. Even if you eat one of these meals on a regular basis, it will not be enough to help you fight the flu or other infections. Pay attention to serving sizes and suggested daily intakes to avoid getting too much of one vitamin and not enough of others. Eating well is a good place to start, but there are additional things you can do to protect yourself and your family from the flu, cold, and other ailments. Begin with these flu preventative nutrition tips, then move on to other great daily habits that will boost your immune, e.g. exercise, reduce stress, and live slowly and holistically. We are committed to serving you the most natural and effective functional food formulas out there.
Summary
Functional Foods are foods designed with scientific intelligence and are intended for special health uses. They currently hold the answer to many common health issues or deficiencies and may be designed as: foods for immune, foods for inflammation, foods for brain, foods for mood, and many more subcategories. See the comparison chart below and learn more about how functional foods compare to supplements. Visit our online healthy food store and discover more about this or the rest of our functional nutrition products.
[sp_easyaccordion id=”15878″]
A Word From MILESTONE®
MILESTONE® Food for your Genes uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
- Somerville VS, Braakhuis AJ, Hopkins WG. Effect of Flavonoids on Upper Respiratory Tract Infections and Immune Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv Nutr. 2016;7(3):488-497. Published 2016 May 16. doi:10.3945/an.115.010538[↩]
- Rivlin RS. Historical perspective on the use of garlic. J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3s):951S-4S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.3.951S. PMID: 11238795.[↩]
- Borlinghaus J, Albrecht F, Gruhlke MC, Nwachukwu ID, Slusarenko AJ. Allicin: chemistry and biological properties. Molecules. 2014 Aug 19;19(8):12591-618. doi: 10.3390/molecules190812591. PMID: 25153873; PMCID: PMC6271412.[↩]
- Allan GM, Arroll B. Prevention and treatment of the common cold: making sense of the evidence. CMAJ. 2014;186(3):190-199. doi:10.1503/cmaj.121442[↩]
- Regulation Of Innate Immune Recognition Of Viral Infection By Epigallocatechin Gallate[↩]
- Lakhan SE, Ford CT, Tepper D. Zingiberaceae extracts for pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr J. 2015;14:50. Published 2015 May 14. doi:10.1186/s12937-015-0038-8[↩]
- Pourmasoumi M, Hadi A, Rafie N, Najafgholizadeh A, Mohammadi H, Rouhani MH. The effect of ginger supplementation on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytomedicine. 2018 Apr 1;43:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.043. Epub 2018 Mar 19. PMID: 29747751.[↩]
- Wang S, Zhang C, Yang G, Yang Y. Biological properties of 6-gingerol: a brief review. Nat Prod Commun. 2014 Jul;9(7):1027-30. PMID: 25230520.[↩]
- Mashhadi NS, Ghiasvand R, Askari G, Hariri M, Darvishi L, Mofid MR. Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of ginger in health and physical activity: review of current evidence. Int J Prev Med. 2013;4(Suppl 1):S36-S42. [↩]
- Yvette Porter, Antioxidant properties of green broccoli and purple-sprouting broccoli under different cooking conditions, Bioscience Horizons: The International Journal of Student Research, Volume 5, 2012, hzs004, https://doi.org/10.1093/biohorizons/hzs004[↩]
- Vasanthi HR, Mukherjee S, Das DK. Retraction Notice To: Potential Health Benefits of Broccoli- A Chemico-Biological Overview. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009 Jun;9(6):749-59. doi: 10.2174/138955709788452685. Retraction in: Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(13):1796. PMID: 19519500.[↩]
- Abdel-Aal el-SM, Akhtar H, Zaheer K, Ali R. Dietary sources of lutein and zeaxanthin carotenoids and their role in eye health. Nutrients. 2013;5(4):1169-1185. Published 2013 Apr 9. doi:10.3390/nu5041169[↩]
- Chandran B, Goel A. A randomized, pilot study to assess the efficacy and safety of curcumin in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Phytother Res. 2012 Nov;26(11):1719-25. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4639. Epub 2012 Mar 9. PMID: 22407780.[↩]
- McFarlin BK, Venable AS, Henning AL, et al. Reduced inflammatory and muscle damage biomarkers following oral supplementation with bioavailable curcumin. BBA Clin. 2016;5:72-78. Published 2016 Feb 18. doi:10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.02.003[↩]
- Ghosh S, Banerjee S, Sil PC. The beneficial role of curcumin on inflammation, diabetes and neurodegenerative disease: A recent update. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Sep;83:111-24. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.05.022. Epub 2015 Jun 9. PMID: 26066364.[↩]
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/[↩]
- Carr AC, Maggini S. Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients. 2017 Nov 3;9(11):1211. doi: 10.3390/nu9111211. PMID: 29099763; PMCID: PMC5707683.[↩]