- Getting Started
-
by k.mammasis
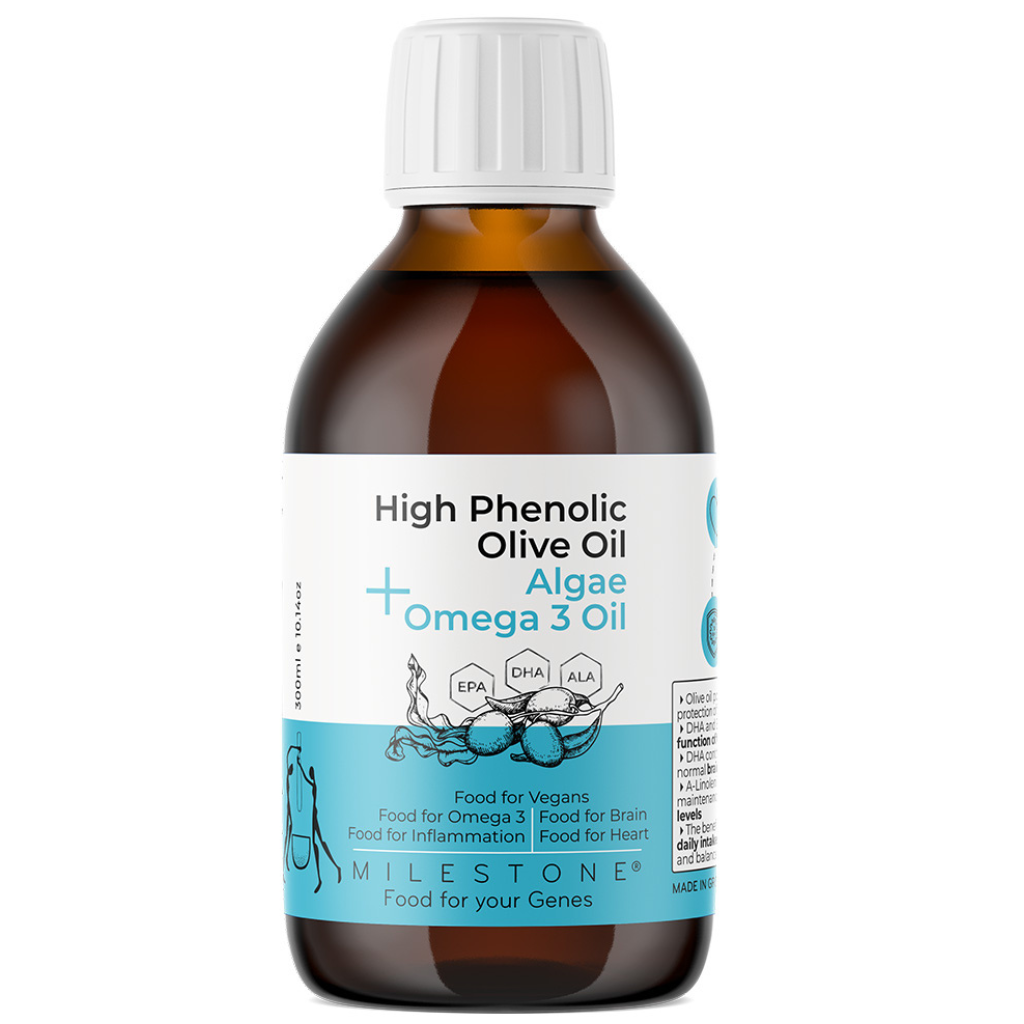
Olive oil contains a very specific type of Omega 3s
Typically, olive oil contains a negligible amount of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is an essential omega-3 fatty acid. ALA is important for maintaining good health, but the body cannot produce it on its own and must obtain it from the diet.
While olive oil is a healthy fat that contains many beneficial compounds, such as monounsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants, it is not a significant source of ALA, and our high phenolic olive oil breaks that barrier. If you are looking to increase your intake of ALA, it is also recommended to consume foods such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
An innovative olive oil offering a full range of Omega-3s
This is the 1st functional food in the world to offer you a full range of Omega 3s (ALA + EPA + DHA) in a single shot. It is a medical-grade olive oil very high in biactive compounds and omega-3, specifically designed for promoting heart and brain health. Formulated to combine plant-based healthy fatty acids synergistically, it also contains bioactive polyphenols (hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, oleocanthal, oleacin and more), Omega 6 and Omega 9 in an unmatched food combination created to meet your full daily nutritional needs.