- Getting Started
-
by k.mammasis
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in a variety of foods, particularly in algae, and fatty fish. They are also present in some plant-based sources such as olive seeds, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
Other dietary sources of omega-3 fatty acids include
- Fortified foods such as eggs, milk, and yogurt
- Omega-3 supplements such as fish oil, krill oil, and algae oil
- Grass-fed animal products such as meat and dairy, contain higher amounts of omega-3 fatty acids than conventionally raised animals.

It’s important to note that the specific types of omega-3 fatty acids found in different sources can vary. For example, fish and fish oil contain EPA and DHA, while plant-based sources such as olive oil contain only ALA. Algae, however, contains both EPA and DHA, but not ALA, which the body can convert into EPA and DHA, but the conversion rate is relatively low.
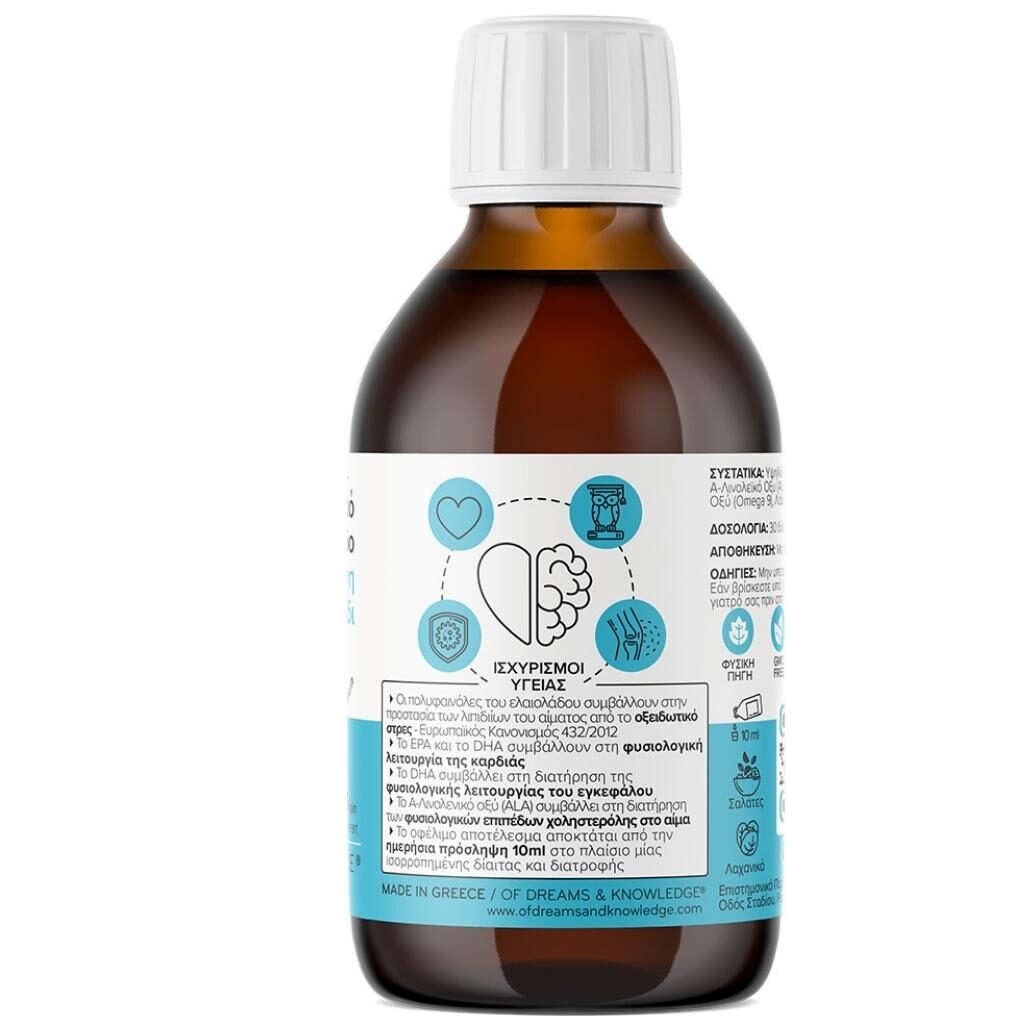
The best Vegan Omega-3s + natural polyphenols and monounsaturated fatty acids
Our High Phenolic Olive + Algae Vegan Omega 3 Oil (EPA DHA ALA) is designed as the optimum functional food for the brain and heart. Formulated to combine plant-based healthy fatty acids synergistically, it offers you nature’s most formidable spectrum of vegan Omega 3 in eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). It also contains Bioactive Polyphenols (hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, oleaocanthal, oleacin and more), Omega 6 and Omega 9 in a healthy food combination created to meet your full daily nutritional needs.
One bottle contains the EPA and DHA equivalent of over 100 anchovy fish. It contains the most natural form of Omega 3s, as extracted from algae grown under fermentation in controlled resource-efficient conditions. It is the most potent natural combination for EPA, DHA (algae) and ALA (olive oil) that exists in the market. 50 times more anti-oxidants than common olive oil.